Key Points
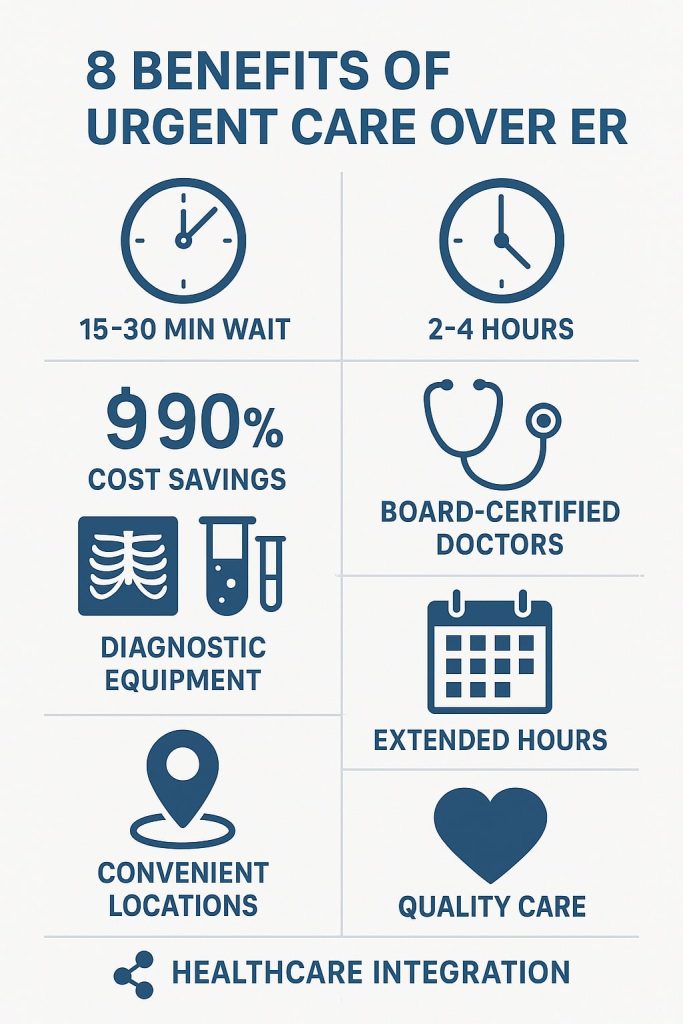
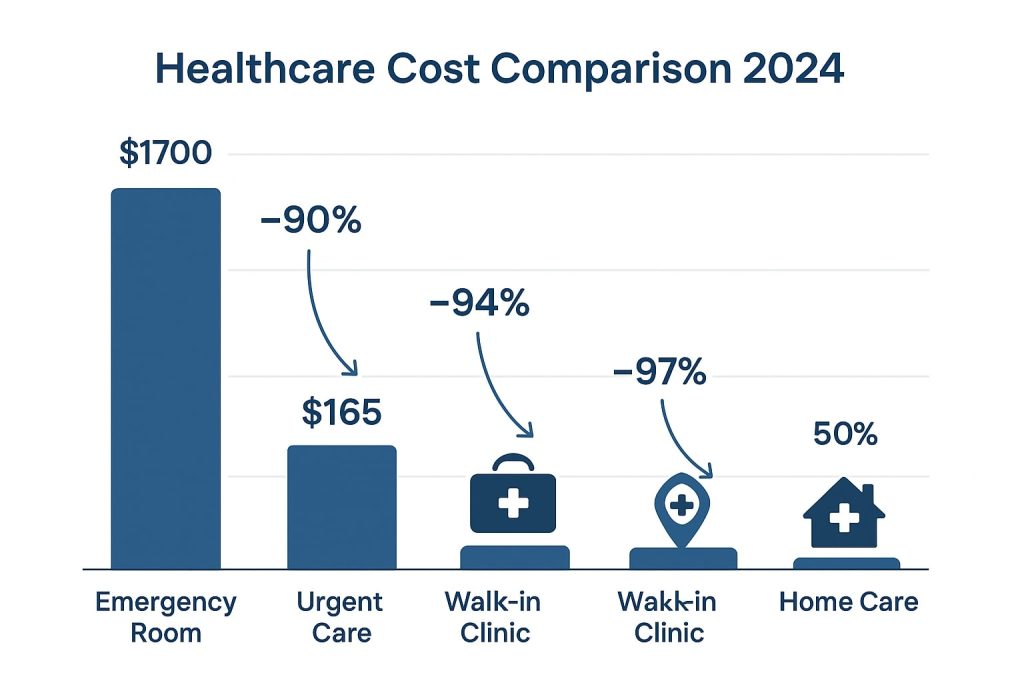
- Cost savings of up to 90% compared to emergency room visits, with urgent care averaging $165 versus $1,700 for ER visits, making healthcare more accessible for families and individuals.
- Dramatically reduced wait times averaging 15-30 minutes at urgent care centers compared to 2-4 hours in emergency departments, allowing patients to receive timely treatment and return to their daily activities.
- Comprehensive medical services including on-site diagnostics, laboratory testing, and advanced treatment capabilities that rival hospital emergency departments for non-life-threatening conditions.
The American healthcare landscape has undergone significant transformation in recent years, with urgent care centers emerging as a vital bridge between primary care and emergency medicine. As healthcare costs continue to rise and emergency department overcrowding becomes increasingly problematic, understanding when and why to choose urgent care over emergency rooms has become essential knowledge for every healthcare consumer.
Recent data from the Urgent Care Association reveals that urgent care centers experienced a 60% increase in visits from 2019 to 2020, highlighting their growing importance in the healthcare ecosystem [1]. This growth reflects not just convenience, but genuine advantages that urgent care centers offer over traditional emergency departments for a wide range of medical conditions.
The decision between urgent care and emergency room care often comes down to understanding the appropriate level of care needed for specific medical situations. While emergency departments remain essential for life-threatening conditions, urgent care centers have proven highly effective for the vast majority of acute medical needs that don't require emergency intervention.
Understanding the Healthcare Delivery Spectrum
Modern healthcare operates on a spectrum of care intensity, from routine primary care appointments to life-saving emergency interventions. Urgent care centers occupy a crucial middle ground, providing immediate access to medical care for conditions that are too serious to wait for a primary care appointment but don't require the intensive resources of an emergency department.
This positioning allows urgent care centers to optimize their operations for efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and patient satisfaction in ways that emergency departments, with their focus on critical care, cannot match. Understanding this distinction helps patients make informed decisions about where to seek care for different types of medical issues.
The Evolution of Urgent Care
Urgent care as a medical specialty has evolved significantly since its inception in the 1970s. Modern urgent care centers combine the accessibility of walk-in clinics with the medical sophistication of hospital-based care, creating a unique healthcare delivery model that addresses many of the gaps in traditional healthcare systems.
Today's urgent care centers are staffed by board-certified physicians, nurse practitioners, and physician assistants who specialize in acute care medicine. They're equipped with advanced diagnostic equipment and maintain protocols for seamless transfer to emergency departments when higher levels of care are needed.
1. Substantial Cost Savings and Financial Accessibility
The financial advantages of urgent care over emergency room visits represent one of the most compelling reasons for choosing this care option. Recent analysis shows that urgent care visits cost approximately 90% less than equivalent emergency department visits, with average costs of $165 for urgent care compared to $1,700 for emergency room care [2].
Insurance Coverage and Out-of-Pocket Costs
Most health insurance plans recognize the value proposition of urgent care and structure their coverage to encourage its use. Typical insurance scenarios include:
- Urgent care copays: $20-$50 for most insurance plans
- Emergency room copays: $100-$500, often with additional deductibles
- Uninsured patients: Urgent care centers typically offer transparent pricing and payment plans
- High-deductible health plans: Urgent care visits often fall below deductible thresholds
Hidden Costs of Emergency Department Visits
Emergency department billing often includes multiple components that can significantly increase total costs:
- Facility fees for emergency department use
- Separate physician fees for emergency medicine specialists
- Additional charges for diagnostic tests and procedures
- Potential hospital admission costs if observation is required
Urgent care centers typically provide bundled pricing that includes all services provided during the visit, making costs more predictable and manageable for patients.
Economic Impact on Healthcare System
The cost-effectiveness of urgent care extends beyond individual patient savings to broader healthcare system benefits. Studies show that urgent care centers reduce total healthcare spending by diverting appropriate cases from more expensive emergency departments, helping to control overall healthcare inflation [3].
2. Dramatically Reduced Wait Times and Improved Access
Wait times represent one of the most significant practical differences between urgent care centers and emergency departments. While emergency departments must prioritize patients based on medical acuity, urgent care centers can typically see patients in the order of arrival, leading to much shorter and more predictable wait times.
Current Wait Time Statistics
Recent data reveals striking differences in wait times:
- Urgent care centers: Average wait time of 15-30 minutes
- Emergency departments: Average wait time of 2-4 hours for non-emergency cases
- Peak time variations: Urgent care wait times remain relatively stable, while ER wait times can extend to 6+ hours during busy periods
Factors Affecting Wait Times
Several factors contribute to shorter wait times at urgent care centers:
- Focused patient population: Urgent care sees patients with similar acuity levels
- Streamlined processes: Operations optimized for efficiency rather than critical care
- Predictable staffing: Staffing levels matched to typical patient volumes
- Limited scope: Focus on treatable conditions reduces complex case management
Impact on Patient Experience
Shorter wait times translate to numerous patient benefits:
- Reduced time away from work or family responsibilities
- Less anxiety and stress associated with waiting for care
- Faster resolution of painful or uncomfortable symptoms
- Improved overall satisfaction with healthcare experience
3. Comprehensive On-Site Diagnostic Capabilities
Modern urgent care centers have invested heavily in diagnostic equipment and capabilities, allowing them to provide comprehensive evaluation and treatment for a wide range of conditions without requiring patients to visit multiple locations or wait for off-site test results.
Advanced Imaging Services
Many urgent care centers now offer:
- Digital X-ray systems: For fractures, sprains, and chest conditions
- Ultrasound capabilities: For soft tissue injuries and certain internal conditions
- CT scanning: Available at larger urgent care facilities for more complex cases
- Immediate results: On-site interpretation by qualified radiologists or trained physicians
Laboratory Testing and Point-of-Care Diagnostics
Urgent care centers typically provide:
- Complete blood count (CBC) and basic metabolic panels
- Urinalysis for kidney and bladder conditions
- Rapid strep tests and flu testing
- Pregnancy testing and basic reproductive health screening
- Drug screening and occupational health testing
Electrocardiogram (EKG) and Cardiac Monitoring
Many urgent care centers can perform and interpret EKGs, allowing them to:
- Evaluate chest pain and cardiac symptoms
- Monitor patients with known heart conditions
- Provide baseline cardiac assessments
- Determine when emergency department referral is necessary
Same-Visit Results and Treatment
The availability of on-site diagnostics means patients can receive:
- Immediate diagnosis and treatment planning
- Prescription medications based on confirmed diagnoses
- Follow-up instructions tailored to specific conditions
- Referrals to specialists when appropriate
4. Board-Certified Physicians and Specialized Training
Urgent care centers are staffed by medical professionals who have chosen to specialize in acute care medicine, bringing focused expertise to the treatment of urgent medical conditions. This specialization often results in more efficient and effective care for the types of conditions commonly seen in urgent care settings.
Physician Qualifications and Training
Urgent care physicians typically have:
- Board certification in family medicine, internal medicine, or emergency medicine
- Additional training in urgent care medicine and acute care protocols
- Experience in both outpatient and emergency medicine settings
- Continuing education focused on urgent care best practices and emerging treatments
Nursing and Support Staff Expertise
Urgent care centers employ:
- Nurse practitioners and physician assistants with acute care training
- Registered nurses experienced in urgent care protocols
- Medical assistants trained in urgent care-specific procedures
- Radiology technicians for on-site imaging services
Quality Assurance and Medical Oversight
Reputable urgent care centers maintain:
- Medical director oversight of all clinical operations
- Regular quality assurance reviews and improvement initiatives
- Standardized protocols for common conditions and procedures
- Continuous staff training and competency assessment
5. Extended Hours and Convenient Locations
Urgent care centers are designed around patient convenience, offering extended hours and accessible locations that make healthcare available when and where patients need it most. This accessibility represents a significant advantage over both traditional primary care and emergency departments.
Operating Hours and Availability
Most urgent care centers offer:
- Extended weekday hours: Often 8 AM to 8 PM or later
- Weekend availability: Saturday and Sunday service
- Holiday coverage: Many centers remain open during holidays
- No appointment necessary: Walk-in service for immediate needs
Strategic Location Planning
Urgent care centers are typically located:
- In retail and commercial areas with easy access and parking
- Near residential communities for convenience
- Along major transportation routes
- In areas underserved by primary care physicians
Accessibility Features
Modern urgent care centers prioritize accessibility through:
- ADA-compliant facilities and equipment
- Multiple language services and interpretation
- Electronic health record integration with other providers
- Online check-in and wait time monitoring
6. Streamlined Treatment for Common Conditions
Urgent care centers excel at treating the types of medical conditions that account for the majority of non-emergency acute care needs. Their focus on these common conditions allows them to develop highly efficient treatment protocols and maintain the supplies and equipment needed for optimal care.
Respiratory Conditions
Urgent care centers are well-equipped to treat:
- Upper respiratory infections: Colds, flu, and sinus infections
- Bronchitis and pneumonia: With on-site chest X-rays and treatment
- Asthma exacerbations: Including nebulizer treatments and medication adjustments
- Allergic reactions: From mild to moderate severity
Musculoskeletal Injuries
Common orthopedic conditions treated include:
- Sprains and strains: With immediate imaging and treatment
- Minor fractures: Diagnosis, stabilization, and referral coordination
- Back pain: Evaluation and conservative treatment options
- Sports injuries: Specialized protocols for athletic injuries
Skin and Wound Care
Urgent care centers provide:
- Laceration repair: Suturing and wound closure techniques
- Burn treatment: For first and second-degree burns
- Skin infections: Diagnosis and antibiotic treatment
- Rash evaluation: Including allergy testing and treatment
Gastrointestinal Issues
Treatment capabilities include:
- Nausea and vomiting: IV hydration and anti-nausea medications
- Abdominal pain: Evaluation and conservative treatment
- Diarrhea and dehydration: Fluid replacement and medication
- Food poisoning: Supportive care and symptom management
7. Preventive Care and Health Maintenance Services
Many urgent care centers have expanded their services beyond acute care to include preventive health services, making them valuable partners in ongoing health maintenance. This expansion allows patients to address both immediate health concerns and long-term wellness goals in a single, convenient location.
Vaccination and Immunization Services
Urgent care centers commonly provide:
- Annual flu vaccines and seasonal immunizations
- Travel vaccines for international travel
- Routine adult vaccines including tetanus and shingles
- Occupational vaccines required for employment
Health Screenings and Wellness Checks
Available screening services often include:
- Blood pressure monitoring and cardiovascular risk assessment
- Cholesterol testing and lipid panel evaluation
- Diabetes screening and blood glucose monitoring
- Basic physical examinations for employment or school requirements
Occupational Health Services
Many urgent care centers offer:
- Pre-employment physicals and drug screening
- Workers' compensation injury evaluation and treatment
- Return-to-work clearances after illness or injury
- DOT physicals for commercial drivers
8. Seamless Integration with Healthcare Systems
Modern urgent care centers operate as integral components of larger healthcare systems, providing continuity of care and seamless communication with primary care physicians and specialists. This integration ensures that urgent care visits contribute to, rather than disrupt, ongoing healthcare relationships.
Electronic Health Record Integration
Advanced urgent care centers offer:
- Shared medical records with primary care providers
- Real-time communication about urgent care visits
- Medication reconciliation to prevent drug interactions
- Follow-up coordination with existing healthcare providers
Referral Networks and Specialist Access
Urgent care centers maintain:
- Established relationships with local specialists
- Streamlined referral processes for complex conditions
- Direct communication with consulting physicians
- Coordinated care plans for ongoing treatment needs
Hospital Partnerships and Transfer Protocols
When higher levels of care are needed, urgent care centers provide:
- Direct admission protocols to partner hospitals
- Emergency department transfer with complete medical information
- Specialist consultation before transfer when appropriate
- Family communication throughout the transfer process
Making the Right Choice: When to Choose Urgent Care
Understanding when urgent care is the appropriate choice empowers patients to make informed healthcare decisions that optimize both outcomes and costs. The key lies in recognizing the types of conditions that urgent care centers are designed to treat effectively.
Ideal Urgent Care Conditions
Choose urgent care for:
- Minor injuries: Cuts, sprains, minor burns, and simple fractures
- Acute illnesses: Flu, colds, ear infections, and urinary tract infections
- Skin conditions: Rashes, minor infections, and allergic reactions
- Digestive issues: Nausea, vomiting, and mild abdominal pain
- Respiratory problems: Cough, congestion, and mild breathing difficulties
When Emergency Care is Necessary
Seek emergency department care for:
- Life-threatening conditions: Heart attack, stroke, severe trauma
- Severe breathing problems: Difficulty breathing or chest pain
- Major injuries: Severe burns, deep cuts, or suspected internal injuries
- Neurological symptoms: Severe headache, confusion, or loss of consciousness
- Severe allergic reactions: Anaphylaxis or widespread swelling
Decision-Making Framework
When in doubt, consider:
- Severity of symptoms: Life-threatening symptoms require emergency care
- Time sensitivity: Can the condition wait for primary care, or does it need immediate attention?
- Complexity: Does the condition require specialized emergency equipment or procedures?
- Your comfort level: When uncertain, it's always appropriate to seek emergency care
The Future of Urgent Care
The urgent care industry continues to evolve, incorporating new technologies and expanding services to meet changing healthcare needs. Understanding these trends helps patients anticipate how urgent care will continue to improve healthcare accessibility and quality.
Telemedicine Integration
Many urgent care centers now offer:
- Virtual consultations for minor conditions
- Follow-up care via video conferencing
- Prescription management through digital platforms
- Triage services to determine appropriate care levels
Advanced Diagnostic Capabilities
Emerging technologies include:
- Point-of-care testing for rapid diagnosis
- Artificial intelligence for diagnostic assistance
- Advanced imaging capabilities in urgent care settings
- Remote monitoring for chronic condition management
Expanded Service Offerings
Future urgent care centers may include:
- Mental health services and counseling
- Chronic disease management programs
- Specialty care access through telemedicine
- Wellness and prevention programs
Conclusion
The choice between urgent care and emergency room care represents more than just a healthcare decision – it's an opportunity to access high-quality medical care in a way that's both cost-effective and convenient. The eight compelling advantages of urgent care outlined in this guide demonstrate why millions of Americans are choosing urgent care centers for their acute healthcare needs.
From substantial cost savings and reduced wait times to comprehensive diagnostic capabilities and specialized medical expertise, urgent care centers offer a superior healthcare experience for the vast majority of non-emergency medical conditions. The integration of urgent care into broader healthcare systems ensures that choosing urgent care doesn't mean sacrificing continuity of care or quality of treatment.
As healthcare costs continue to rise and access to primary care becomes increasingly challenging, urgent care centers provide a valuable solution that benefits both patients and the broader healthcare system. By understanding when and why to choose urgent care, patients can take control of their healthcare decisions and access the right level of care at the right time and cost.
The future of healthcare lies in providing accessible, high-quality care that meets patients where they are and when they need it. Urgent care centers represent a significant step toward that future, offering a healthcare model that prioritizes both clinical excellence and patient convenience. For non-emergency medical needs, urgent care isn't just an alternative to emergency room care – it's often the better choice.
References:
[1] Urgent Care Association. "2023 Urgent Care Industry White Paper." https://urgentcareassociation.org/wp-content/uploads/2023-Urgent-Care-Industry-White-Paper.pdf
[2] United Healthcare. "What are my care options and their costs?" https://www.uhc.com/member-resources/where-to-go-for-medical-care/care-options-and-costs
[3] Allen, L., Cummings, J.R. "The impact of urgent care centers on nonemergent emergency department visits." Health Services Research, 2021. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/1475-6773.13631
[4] Care Station Medical. "Emergency Room vs. Urgent Care: Which Option Is More Budget Friendly?" https://carestationmedical.com/2024/11/04/emergency-room-vs-urgent-care-which-option-is-more-budget-friendly/








